An in-depth look at Ophthalmic Examination
An Ophthalmic Examination Guide embarked on a complex yet essential process purposed for sustaining eye health. The guide aims to reveal ocular issues such as cataracts, glaucoma, or macular degeneration amongst many others. By elucidating each step involved, it simplifies the process of eye examination.
Setting the Groundwork for Examination
A preliminary understanding of the patient’s history plays a vital role in setting the tone for examination. Details regarding symptoms, ocular history, prescribed and over-the-counter medicines, lifestyle factors, and allergies provide a solid base for the entire process.
Assessment of Visual Acuity
The consecutive stage involves assessing visual acuity employing a Snellen chart. The test result serves as an indicator of one’s ability to discern fine details, thus aids in disclosing potential ocular disorders and tracking overall visual performance.
Tests before Actual Examination
Several tests are conducted pre-examination to determine the patient’s depth perception, color vision, pupillary responses and ocular motility. This encompasses a complete view of the patient’s visual health.
Examination for Refraction
The refraction test aids in detecting refractive aberrations within the eye. It provides essential data, enabling ophthalmologists to suggest suitable eyewear or contact lenses for error correction.

Measuring Intraocular Pressure
Intraocular Pressure (IOP) measurement significantly helps in diagnosing glaucoma. IOP denotes the pressure within the eye, and higher values may hint at possible damage to the optic nerve.
Examination of Visual Field
Visual field tests shed light on the peripheral vision – the complete vertical and horizontal expanse visible to the eye. This step is integral for delineating optic nerve damage and other neurological disorders.
External and Internal Eye Check
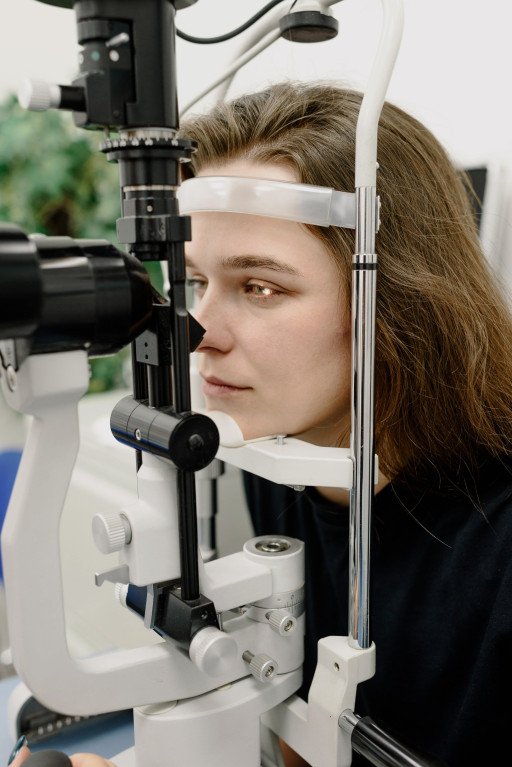
Having tools like ophthalmoscopes and slit lamps at their disposal, ophthalmologists thoroughly study both external and internal aspects of the eye. The appraisal of anterior structures like lenses, corneas, eyelids, iris, and conjunctiva forms part of the external eye check. On the other hand, the internal examination focuses on posterior structures, primarily the retina, vitreous humor, and optic nerve, which are key in severe conditions like retinal detachment and macular degeneration.
Summing Up
The Ophthalmic Examination Guide plays a pivotal role in diagnosing eye diseases and maintaining optimal ocular health by employing careful and precise methods. It presents an elaborate picture of eye-related conditions, thereby assisting diagnosis, treatment, and management of ocular health. Get to know more about it essential chapters advanced scripps ophthalmology guide.
Related Posts
- The Expert Eye Care Services of Dr. Epstein: Unraveling the Art of Optometry
- Comprehensive Guide to Pediatric Eye Clinic: Understanding Children’s Eye Health
- Excellence in Eye Care: 5 Highlights of the Wilmer Eye Institute’s Services
- The Unrivalled Expertise of Norwich Eye Doctors: Comprehensive Guide
- 7 Essential Chapters to Mastering the Advanced Scripps Ophthalmology Guide